3.
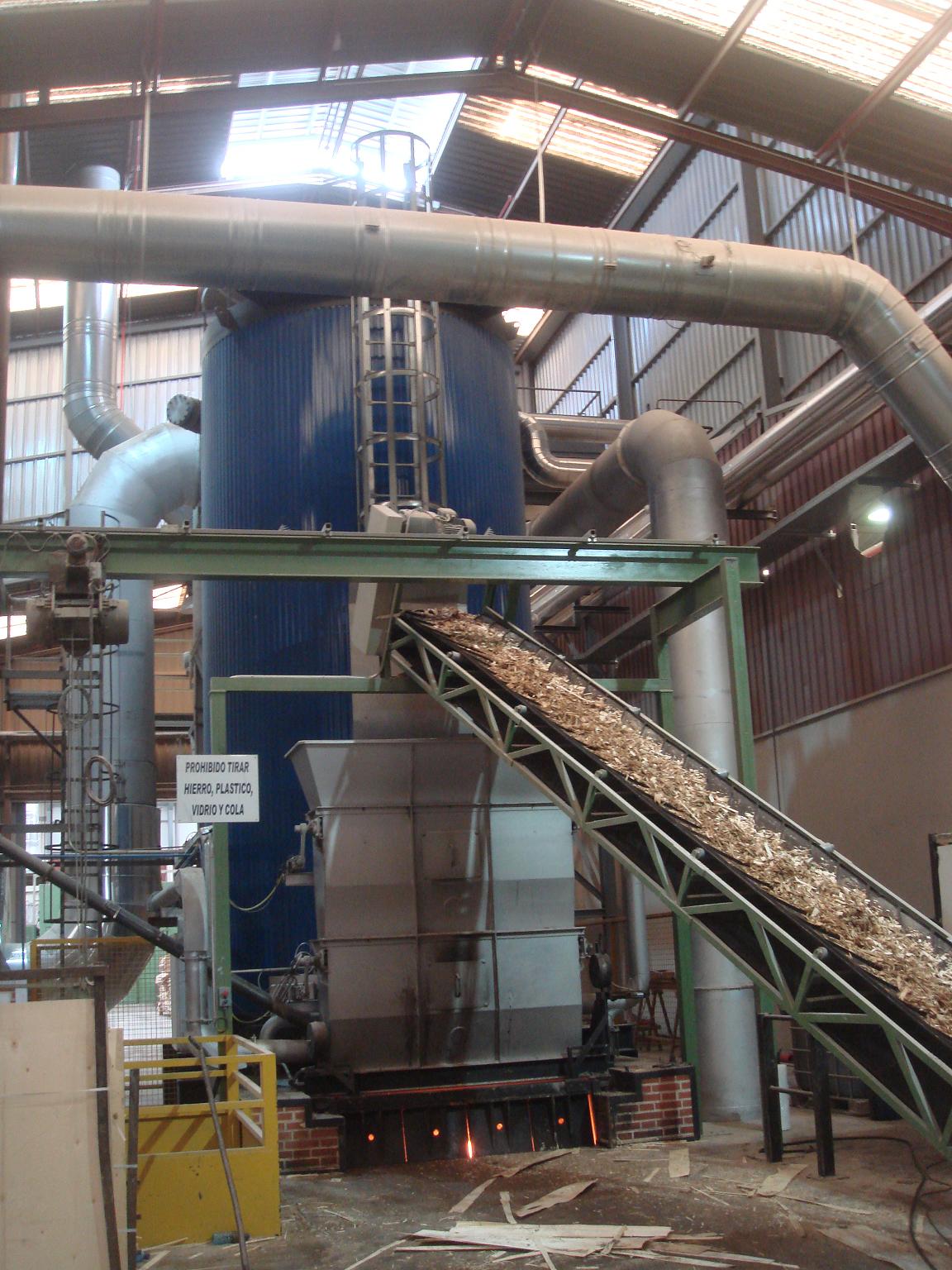
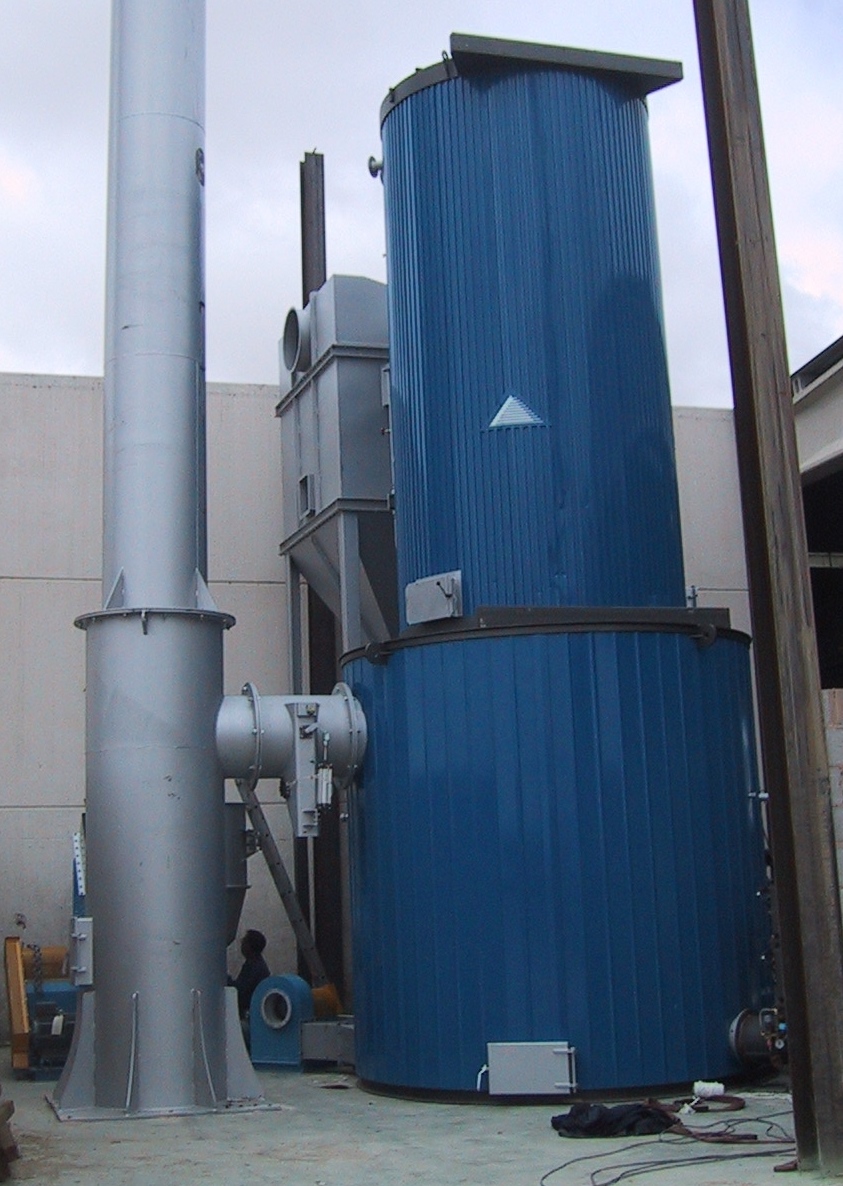
Biomass heater
- Fuel saving by substitution of fossil fuels
- Leading technology
- Low energy consumption
- High reliability
- Large heating surface
- Specific designs for each type of fuel
- Emissions treatment
- Telemanagement
Biomass heaters:
- Thermal fluid
- Hot water
- Superheated water
Thermal energy can be obtained from by-products that the industry itself generates which can be used as fuel, with the consequent saving of fuels derived from petroleum.
Types of combustion chambers:
Depending on the available biomass (source, moisture, composition, grain size, ...):
- Prefabricated, monobloc, vertical or horizontal cylindrical.
- Underground systems:
- Fixed inclined grids
- Mobile grids
Characteristics:
- Standards for design, construction and maintenance UNE 9-310, DIN 4754, VDI 3033
-
 Marking Directive 97/23/CE DEP
Marking Directive 97/23/CE DEP - Indirect Surveillance with intervals of 24 hours supervision (or 72 hours optional)
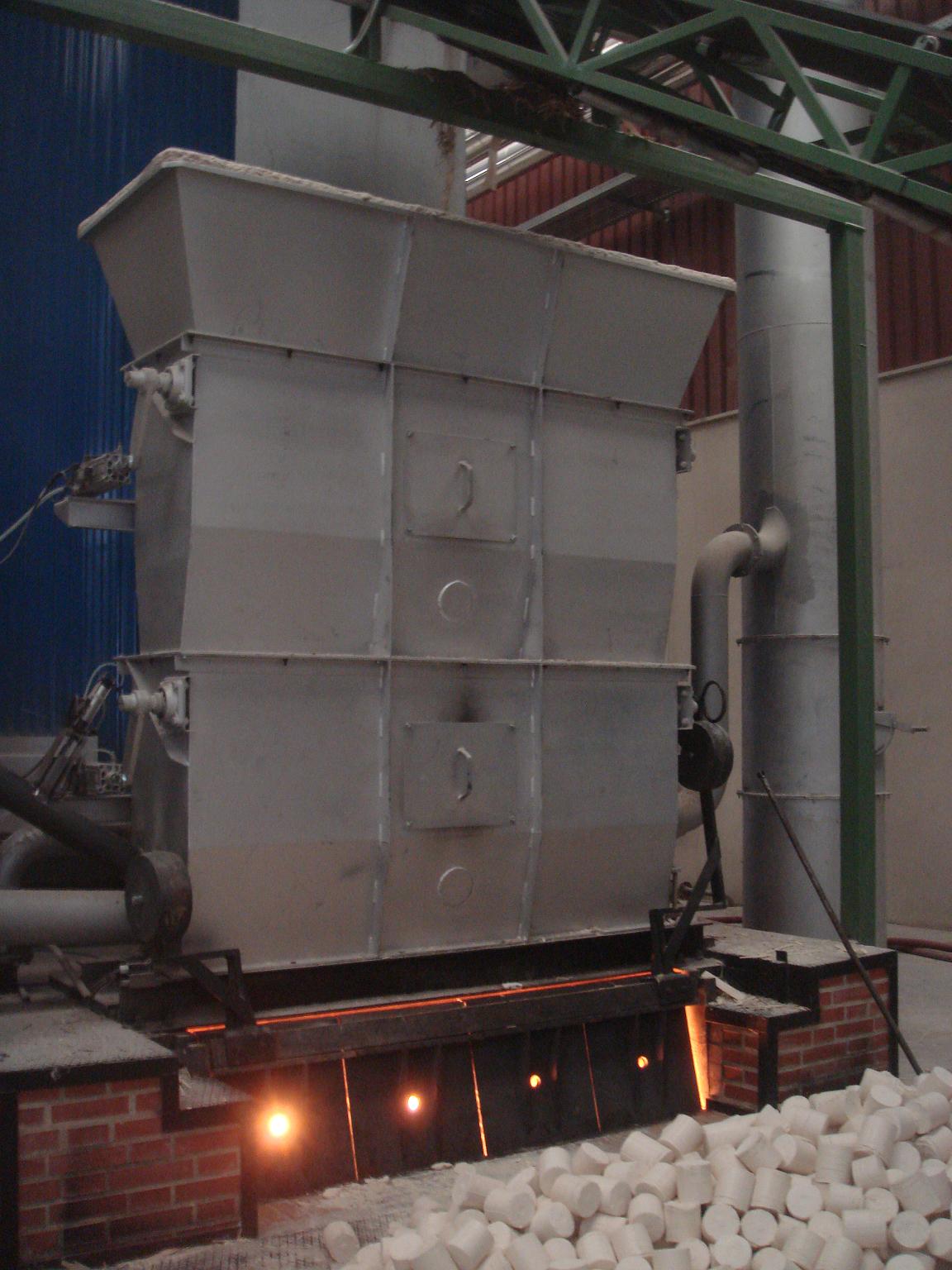
- High velocity and turbulence of the thermal oil
- High heat transfer surface
- Low thermal load
- Oversized combustion chamber
- Vertical construction
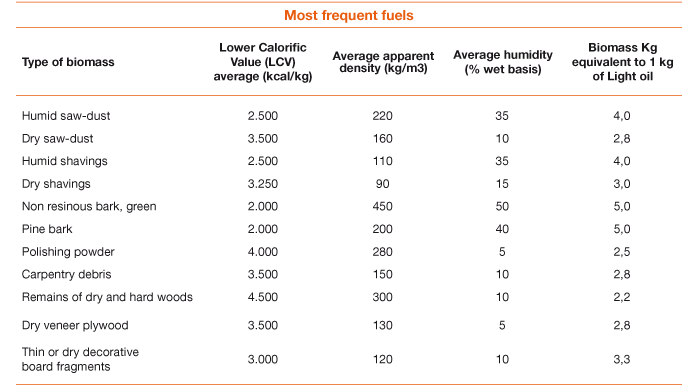
Fuel: sawdust and shavings, veneer, bark, sanding dust, carpentry debris......

Complete systems:
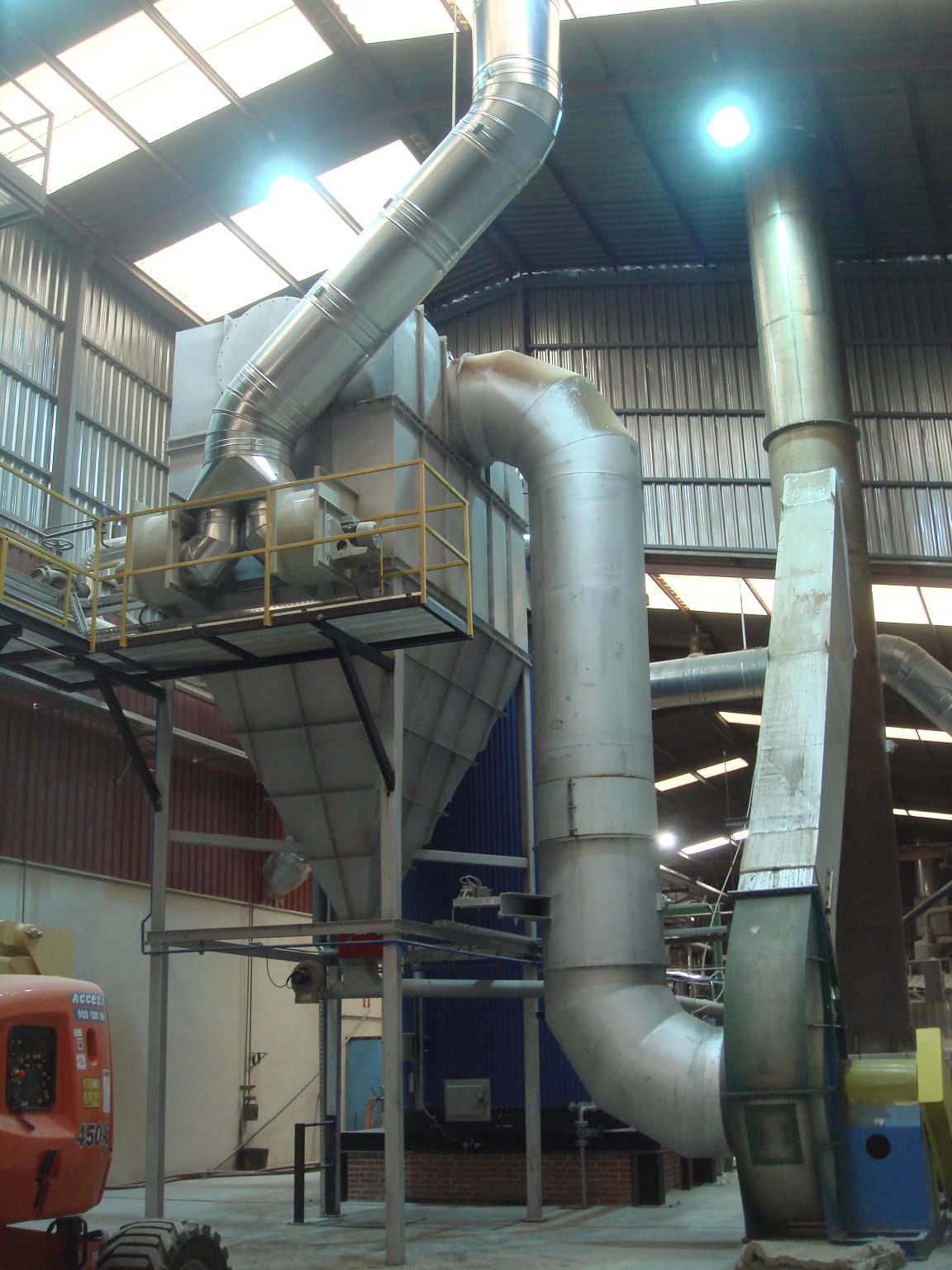
- Silos for fuel storage and heater feeding.
- Multicyclonic separators with high efficiency.
- Economizers
- Automatic feeding
- Automatic cleaning of ashes
- Rotary valves special for high temperature for discharge of unburned
















